Unpacking KiwiStealer: Diving into BITTER APT’s Malware for File Exfiltration
Learn about KiwiStealer capabilities and malware analysis of how it exfiltrates data via HTTP POST requests.

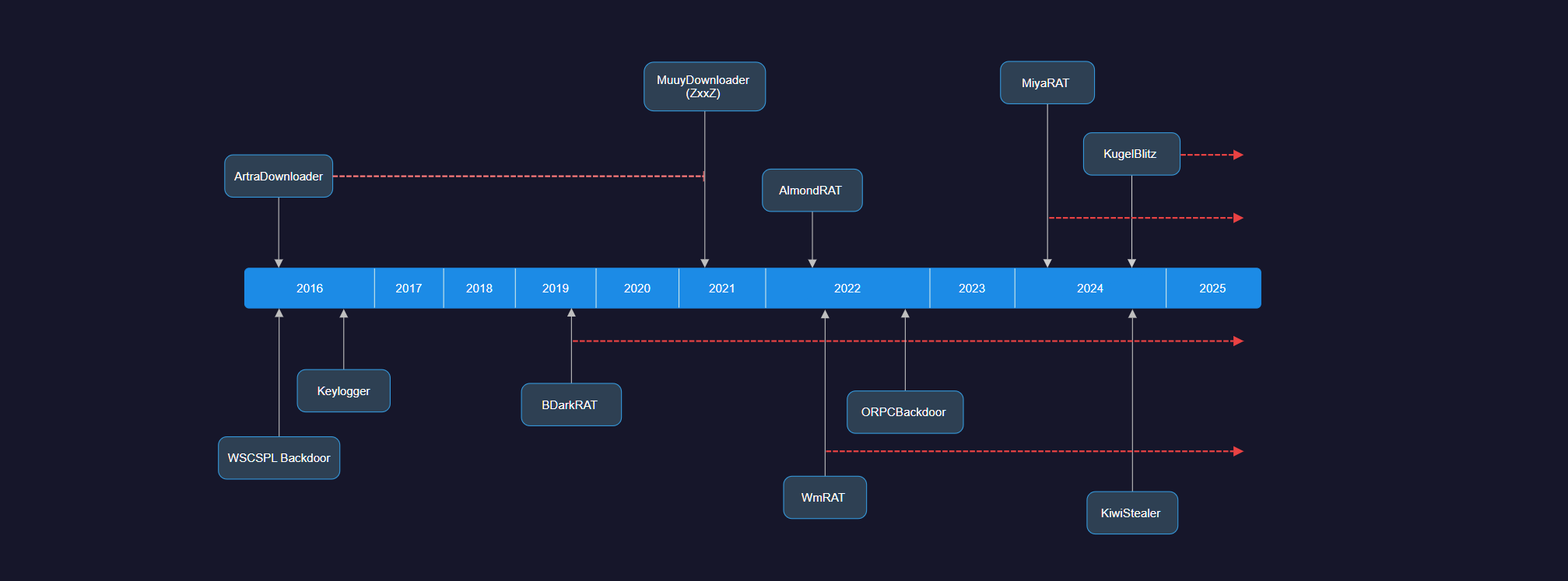
KiwiStealer is a file stealer that was first identified in 2024. The first report on the malware was posted on the platform ctfiot. Subsequent reporting from ThreatRay revealed that the malware was observed being used by the threat group Bitter APT in late 2024. The malware collects some system information before attempting to collect files from specific directories. This blog outlines the malware’s capabilities and how it exfiltrates data via HTTP POST requests. This overview includes:
- Malware Analysis
- Network Traffic Analysis
- Recommendations
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
- MITRE ATT&CK TTPs
Malware Analysis
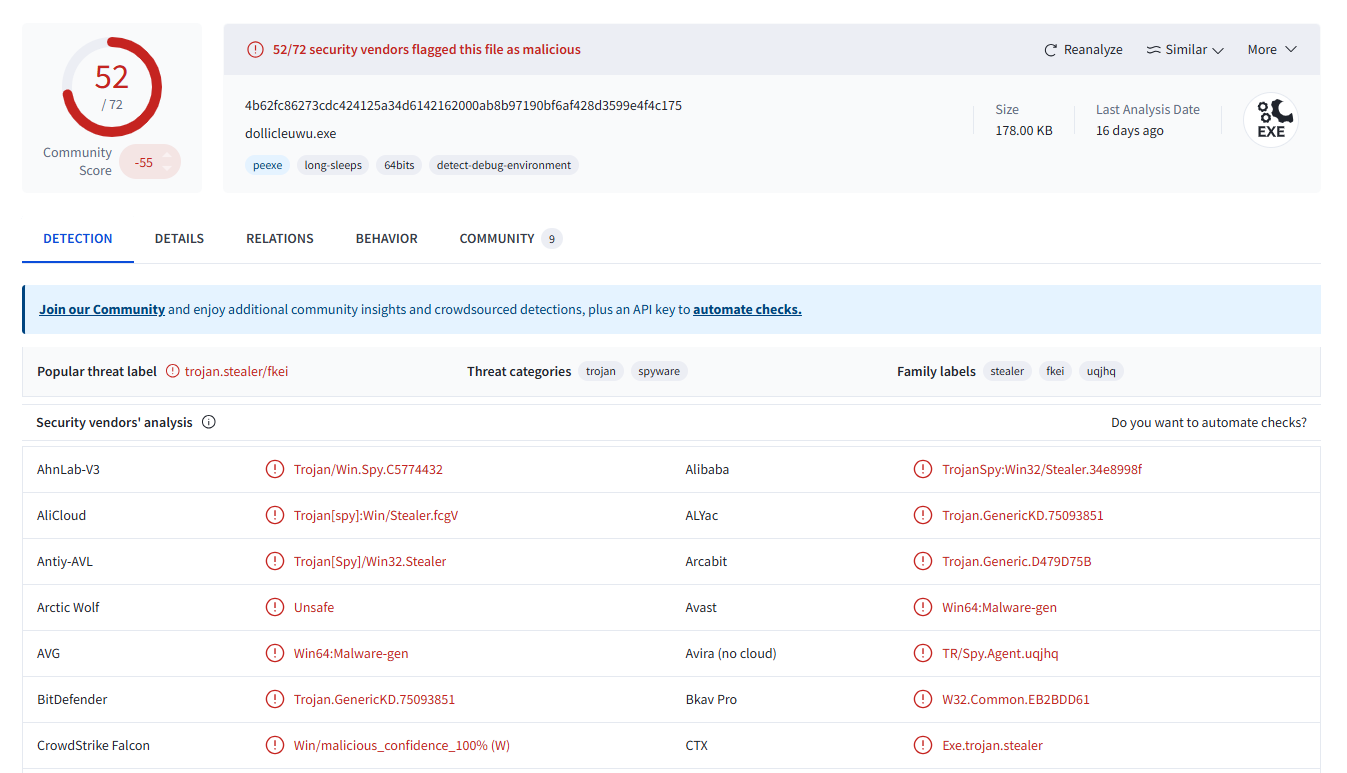
The file analyzed as part of this blog can be found on VirusTotal. The following table shows information about the sample, including hash values.
The malware collects the username and computer name, appending this information to the C2 URI and including it in HTTP requests to the C2 server. The URI is itself hardcoded within the malware and is decoded using string reversal and a modified Caesar Cipher (ROT2). The sample also created a mutex rabadaisunique, to ensure that multiple instances of the malware cannot be executed on a compromised host.
KiwiStealer iterates through several directories to identify files that can be exfiltrated. These directories are shown in the screenshot below.
The malware will only exfiltrate files that are less than 50 MB in size and that have been modified in the last year. The file extensions that the malware targets are outlined in the table below.
After successfully extracting files, the malware appends the file name to a file called winlist.log along with the time it was exfiltrated. When the sample was detonated by a sandbox, two files were exfiltrated, and their names were added to winlist.log.
Network Traffic Analysis
The PCAP for this sample is available on Any.Run.
The malware exfiltrates information to its C2 server via HTTP POST requests. The POST request returns files containing data about the file. The PCAP contains two POST requests. The requests are to the domain ebeninstallsvc[.]com, to the URI /uplh4ppy.php. The request to the domain includes the computer name and user name of the compromised host.
WHOIS data for the domain ebeninstallsvc[.]com shows that it was registered with NameCheap on 2023-10-27 at 07:08:18 UTC.
The first request sends back an RTF file titled 20240712_173213__ukdescribed.rtf to the server. If this file is successfully transmitted to the server, the C2 responds with the response line success.
This RTF document was stored on the desktop and exfiltrated by the malware.
The second POST request sends back an image to the C2 server.
The image can be decoded using CyberChef using the recipe shown in the screenshot below. The picture was extracted from the PCAP using the export functionality within Wireshark.
A larger version of the image is shown below. This particular image was stored on the sandbox and exfiltrated by the malware.
ThreatRay’s report also includes screenshots of other traffic associated with the malware. This particular screenshot contains information about the collected files.
Conclusion
KiwiStealer is a malware that exfiltrates files from compromised machines. The malware targets a specific set of file extensions and only attempts to exfiltrate files that have been modified in the past year and are less than 50MB in size. Unlike other malware variants that have advanced capabilities, KiwiStealer is a relatively simple malware whose sole purpose is to exfiltrate files.
Recommendations
Methods to mitigate the risks posed by malware such as KiwiStealer include:
- Deploy EDR/AV solutions
- EDR or AV solutions can detect malicious process chains and anomalous activity that may be indicative of a malware infection.
- User Education
- Users can help mitigate the risk of information-stealing malware infections by avoiding suspicious websites and using authorised software in corporate environments.
Indicators of Compromise
The table below contains a list of KiwiStealer network IOCs that have been identified and added to the Pulsedive platform. This data can be queried in Pulsedive using the Explore query threat="KiwiStealer" and is available for export in multiple formats (CSV, STIX 2.1, JSON).
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs
References